India

Barbados

USA

Australia

Bangladesh

Canada
Georgia

Kazakhstan

Nepal

Russia

Tajikistan

UK

Uzbekistan
Studying overseas can change a student's life by providing them with the chance to enhance their careers, discover different cultures, and receive top-notch instruction. Studying abroad can lead to international chances, regardless of your course of study—undergraduate, graduate, or professional.
No institutions available for Canada
No institutions available for Australia
No institutions available for New Zealand
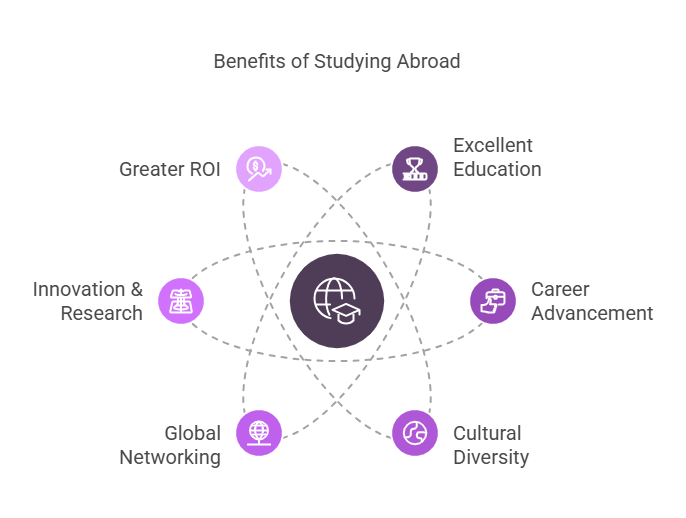
Advantages of International Study
Excellent Education: Gain entry to internationally recognized universities.
Career Advancement: Increased employment opportunities with global exposure.
Cultural Diversity: Get to know different languages, cultures, and viewpoints.
Global Networking: Establish relationships with experts around the world.
Innovation & Research: Availability of top-notch research facilities and cutting-edge technologies.
Greater ROI: A lot of foreign degrees provide great employment prospects and a good return on investment.
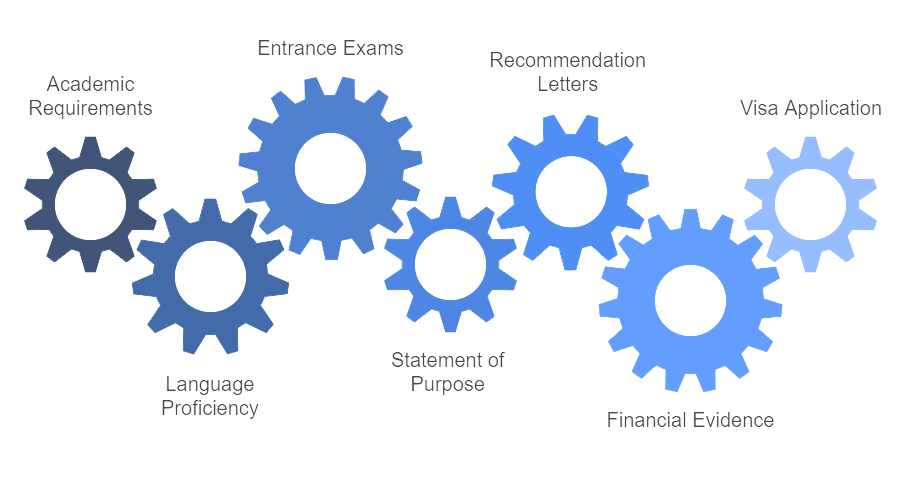
Qualifications and Admissions Procedure
Academic Requirements: Prior qualifications must be at least 60%.
Language Proficiency: PTE, TOEFL, and IELTS scores are necessary.
Entrance Exams: The GRE and GMAT are required for master's programs in some countries.
Statement of Purpose (SOP): Academic and occupational goals must be outlined.
Recommendation Letters (LORs): These should be provided by employers or instructors.
Financial Evidence: Tuition and living expense bank statements are required.
Visa Application: Approval of the student visa is necessary.
Possibilities for Employment While Learning
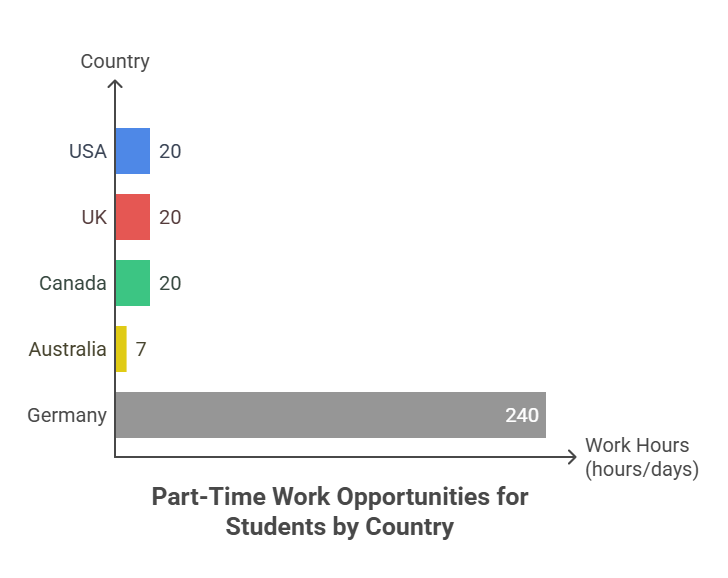
The majority of nations permit full-time employment during breaks and part-time employment while students are enrolled.
USA: 20 hours per week (only F1 Visa holders are eligible for on-campus positions).
UK: 20 hours per week (term), full-time on holidays.
Canada: 20 hours a week, either on or off campus.
Australia: Every day of the week.
Germany: 240 half days or 120 full days annually.
Financial Aid and Scholarships
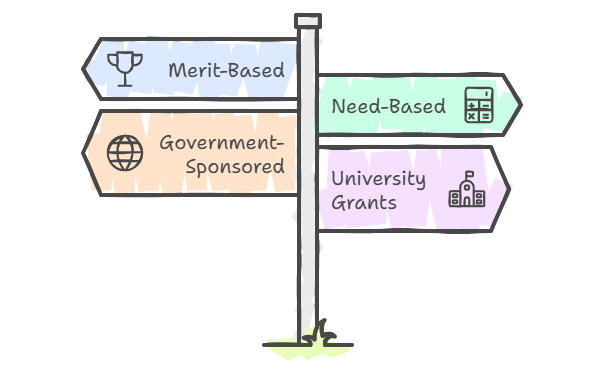
Merit-Based Scholarships: Awarded based on academic excellence.
Need-Based Scholarships: Designed for students requiring financial assistance.
Government-Sponsored Scholarships: Examples include Chevening (UK) and DAAD (Germany).
University Grants: Internal scholarships provided by universities.
Examples of International Scholarships:
- - Fulbright Scholarship (USA)
- - Commonwealth Scholarship (UK)
- - DAAD Scholarships (Germany)
- - Vanier Canada Graduate Scholarship (Canada)
- - Australia Awards Scholarships (Australia)
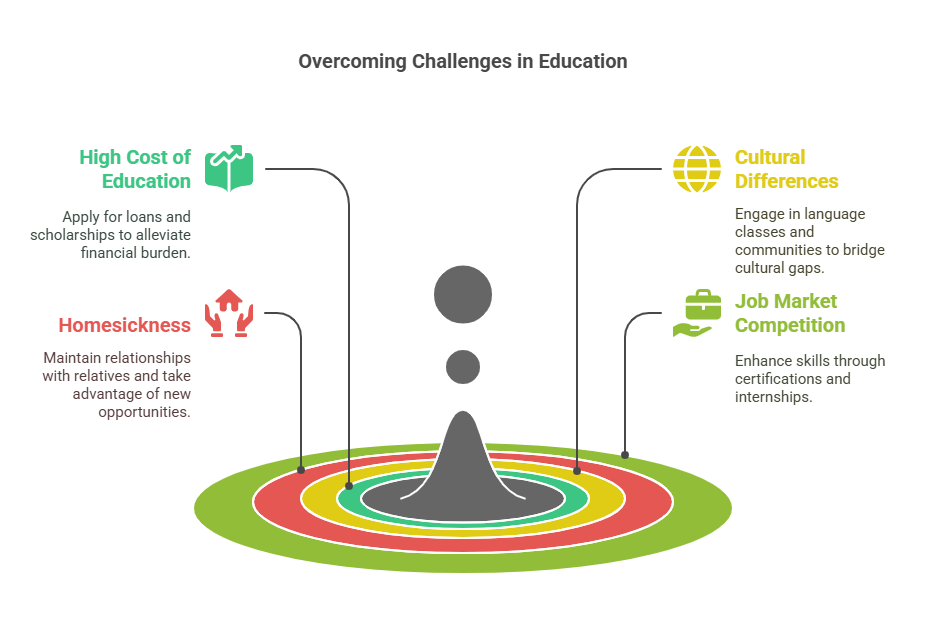
Obstacles and How to Get Past Them
High Cost of Education: Apply for education loans and scholarships.
Cultural Differences: Participate in language classes and student communities.
Homesickness: Maintain relationships with relatives and take advantage of new opportunities.
Job Market Competition: Acquire skill certifications and internships.